|
||
|
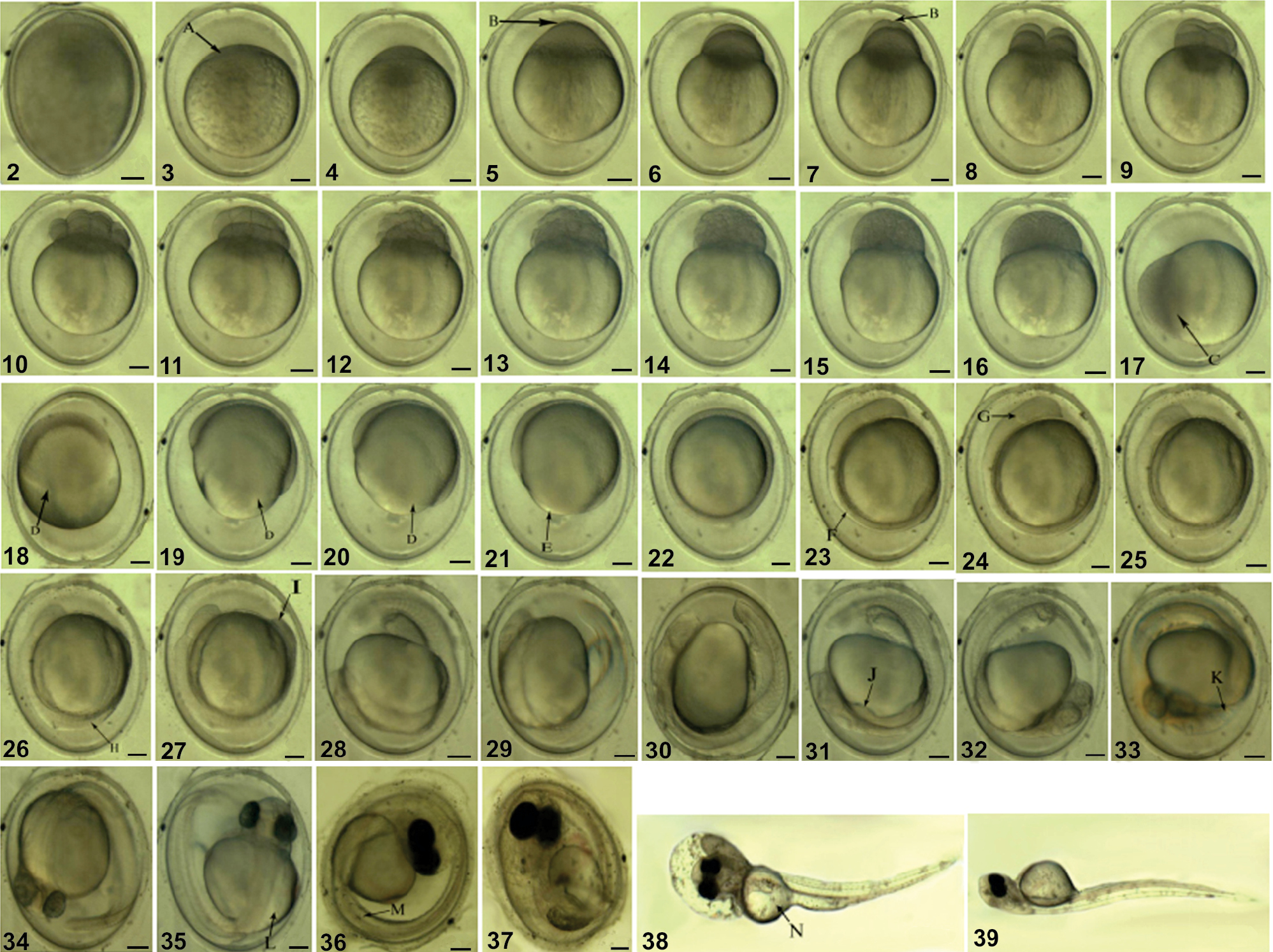
Embryonic development of Pseudorasbora parva: (2) Fertilized egg; (3) The fully-swollen egg (A, blastoderm); (4) Blastodisc formation; (5) The first cleavage furrow (B, cleavage furrow); (6) 2-cell phase; (7) The second cleavage furrow (B, cleavage furrow); (8) 4-cell phase; (9) 8-cell phase; (10) 16-cell phase; (11) 32-cell phase; (12) 64-cell phase; (13) Cellulouse phase; (14) Morula phase; (15) Early blastula phase; (16) Mid-blastula phase; (17) Late blastula phase (C, cells epiboly); (18) Early gastrula phase (D, germ ring); (19) Mid-gastrula phase (D, germ ring); (20) Late gastrula phase (D, germ ring); (21) Neural embryo formation (E, blastopore); (22) Blastopore closed phase; (23) Somites appearance (F, somite); (24) Optic vesicle appearance (G, optic vesicle); (25) Optic capsule appearance; (26) Notochord appearance (H, notochord); (27) Tail bud appearance (I, tail bud); (28) Otic vesicle appearance; (29) Crystalline lenses formation; (30) Muscle function phase; (31) Heart bud appearance (J, heart bud); (32) Heartbeat phase; (33) Otolith appearance (K, otolith); (34) Eye pigment appearance; (35) Pectoral fin bud appearance (L, pectoral fin bud); (36) Body pigment appearance (M, body pigment); (37) Hatching prophase; (38) Hatching phase (N, yolk sac); (39) Newly hatched larva. Scale bars: 2–37 = 0.2 mm, 38–39 = 0.5 mm. |